Telework and Accessing the Workplace
February 7, 2019 SNG Research Brief – Teleworking
SNG Research Brief – Teleworking
Teleworking is not for everyone, nor is it available to everyone in their job. However, a growing number of people telework part or all of their work week. We define telework as working at your job from home in a formal arrangement with the employer during normal working hours, as opposed to simply accessing the workplace remotely on an occasional basis or while traveling.
Teleworking offers tremendous potential for people to be employed in the type of job they want and to live in the community they prefer, but to telework effectively people need robust and reliable broadband connections. So, what is the current state of teleworking and what is its impact on teleworking households and the community? SNG has compiled important teleworking insights from research of over 18,000 households.
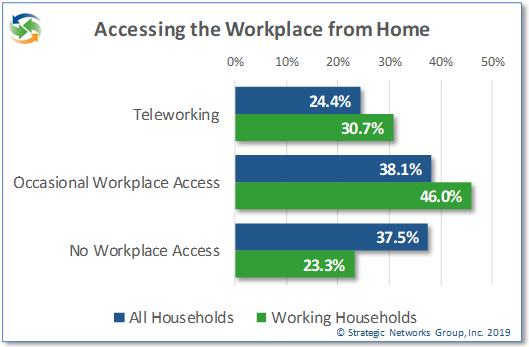
Nearly one in four households (24.4%) include one or more teleworking members. An additional 38% of households access the workplace from home on an occasional basis. These numbers increase to 31% and 46% for employed, working-age households. The vast majority of those employed use home internet for work reasons to some degree.
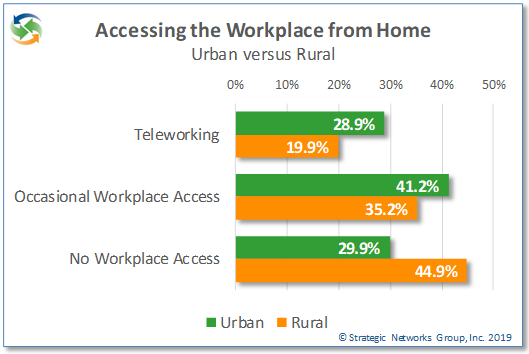
There is a significant difference between urban and rural households in accessing the workplace from home. Occasional workplace access is 6 percentage points lower for rural households, and teleworking is 9 percentage points lower. There can be a number of reasons for this difference, but one factor is the availability and quality of broadband in urban versus rural communities, as discussed in our research brief on household broadband. While teleworking offers the same benefits whether in an urban or rural community, it can be of particular value to rural residents who have a more limited range of local employment opportunities than their urban counterparts.
44% of teleworkers spend at least 4 days per week working from home, with an average of 3.2 days per week teleworking. The average one-way commute avoided is 60 miles (100 km) with almost one-third of teleworker living more than 60 miles from their employer workplace. Those with more distant commutes tend to telework more days per week. Nearly 75% of teleworkers say that reducing their time commuting is a very important benefit. This not only reduces commuting time, but reduces costs for fuel and car maintenance while reducing traffic, road wear, and fuel emissions.
Not just a convenience
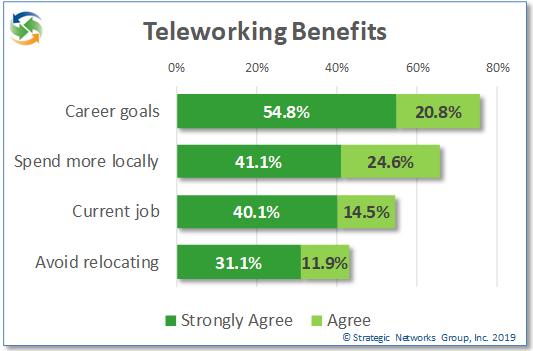
Teleworking is not merely a convenience and cost saving for households, although these are important benefits. More than half of teleworkers strongly agree that their ability to telework in their job helps in achieving their career goals. 40% strongly agree that they would not have their current job were it not for teleworking and 31% strongly agree that they would need to relocate for their job if they could not telework.
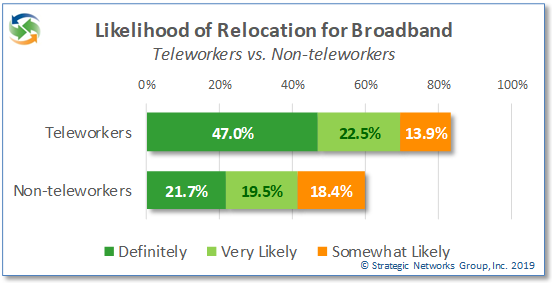
For those currently teleworking, their ability to do so is an important factor in being able to remain in their community while employed in a job that meets their goals. Having access to quality broadband is essential for people to effectively work from their home office. In fact, the likelihood of household relocation to get quality broadband service is more that twice as high for teleworking households than for non-teleworking households, with 47% saying they would definitely relocate for broadband versus 22% of non-teleworkers. (For more on this, please read our research brief on Broadband Importance to Household Location.)
An unsung community asset
The significance of this for communities is that those households who may want to telework and have the opportunity to do so may need to either forgo those employment opportunities or relocate out of the community if they do not have the quality of broadband they need. By the same token, those who may want to locate into the community for its other attractions will be inhibited to do so if the available broadband does not allow them to telework effectively. While teleworking only impacts a portion of the population, it is a significant portion and a lack of quality broadband can have noticeable consequences for attraction and retention of households.
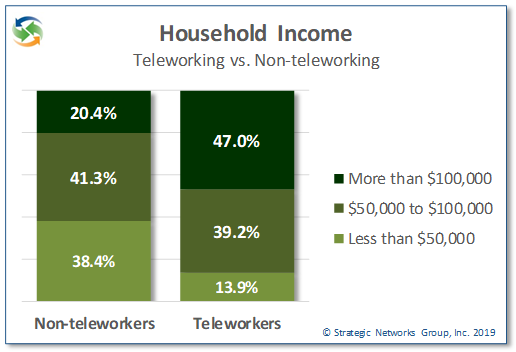
Not only is the teleworking household segment a significant percentage of the community, it is a highly valuable segment. Teleworking households have significantly higher incomes than non-teleworking households, with 47% having a household income of more than $100,000 per year compared to 20% of non-teleworking households. 86% earn more than $50,000 per year.
Households with higher incomes spend more locally, own more valuable properties, and pay higher taxes locally. While communities cannot create teleworking employment opportunities for residents, ensuring that they have the quality broadband needed sets the stage for having more residents telework and stay in the community, as well as attracting new teleworking residents.
Teleworking delivers benefits not only to those teleworking but also to the community by giving residents the option to find or keep the job they want while remaining in their community of choice. By working from home, teleworkers spend more time in their community, buy more locally, and are more engaged in the community. Communities that ensure they have quality, robust broadband provide a platform for teleworking and open up more opportunities for their residents and for attracting new residents.
See what teleworking means for a rural county and how they got the support and funding to build the digital infrastructure they need to thrive – Custer County Broadband Impact and Market Assessment.
Find out more about SNG Solutions for Local Economic Development.